What Is an SPF Record
Learn what an SPF record is, how it works, and why it is essential for protecting your domain and improving email deliverability.
An SPF (Sender Policy Framework) record is a DNS record that defines which mail servers are authorized to send emails on behalf of your domain.
Its main purpose is to prevent email spoofing, where attackers send emails that appear to come from your domain without permission.
How SPF Works
When an email is received, the recipient’s mail server checks the SPF record of the sender’s domain.
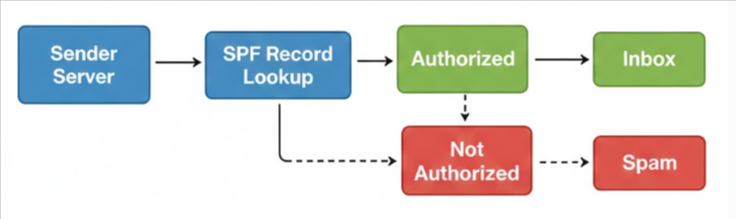
It compares the sending server’s IP address with the list of authorized servers defined in the SPF record.
If the server is authorized, the SPF check passes.
If the server is not authorized, the email may be marked as spam or rejected.
This verification helps inbox providers determine whether the email is legitimate.
Why SPF Is Important
Protects Your Domain
SPF blocks unauthorized servers from sending emails in your name. This reduces phishing attempts and protects your brand reputation.
Improves Deliverability
Domains with valid SPF records are trusted more by inbox providers. This increases the likelihood of emails reaching the inbox.
Reduces Spam Abuse
Unauthorized emails are more likely to be blocked when SPF is configured correctly, preventing spam activity tied to your domain.
Key Takeaway
SPF is a foundational email authentication standard. It verifies that emails sent from your domain are authorized and helps protect against spoofing.
For full protection and best deliverability results, SPF should always be used together with DKIM and DMARC.
Also check
Understanding DNS Records for Email Deliverability
DKIM: What, Why, and How to Set it up?
DMARC: What, Why, and How to Set it up?
Technical Checklist Before Starting Email Warm-up
Did this answer your question?
😞
😐
😁