DKIM: What, Why, and How to Set it up?
What is DKIM, Why DKIM, How to Setup DKIM, and How to Check if DKIM is Verified. Configuring DKIM improves your email deliverability.
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) is an email authentication method that protects your domain from spoofing, phishing, and message tampering. It also improves deliverability and strengthens sender reputation.
This guide explains what DKIM is, how it works, how to set it up, and how to verify it.
What DKIM Does
DKIM adds a digital signature to outgoing emails.
When you send an email:
Your mail server signs the message using a private key
The receiving server retrieves the public key from your domain’s DNS
The signature is verified against the message
If the signature matches, the email is confirmed as authentic and unchanged.
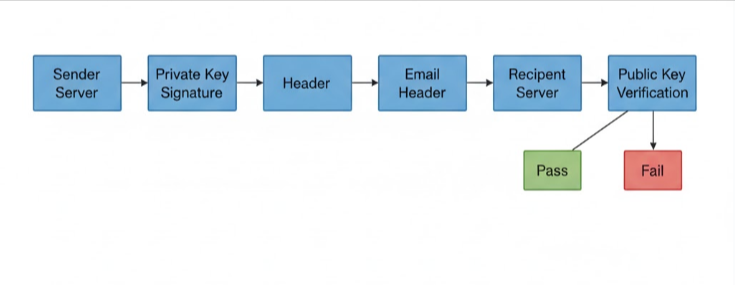
If verification fails, the message may be sent to spam or rejected depending on authentication policies.
Why DKIM Is Important
DKIM:
Prevents attackers from impersonating your domain
Proves message integrity during transit
Improves inbox placement
Strengthens sender reputation
Works with SPF and DMARC to create a complete authentication framework
Emails without valid DKIM signatures are more likely to be flagged as suspicious.
When DKIM Can Be Configured
DKIM can only be set up for custom domains such as: [email protected]
It cannot be configured for free email addresses like gmail.com, outlook.com, or yahoo.com.
Most email providers generate DKIM records inside their admin panel. Some require manual DNS updates.
How to Set Up DKIM
Step 1: Generate the DKIM Key
Log in to your email provider’s admin panel and generate a DKIM key.
For example, in Google Workspace this is done inside the Admin Console.
Step 2: Add the DKIM Record to DNS
Add the generated DKIM key as a TXT record in your domain’s DNS.
Log in to your domain DNS manager
Create a new TXT record
Paste the selector and public key provided
Save changes
DNS updates may take up to 48 hours to propagate.
Step 3: Enable DKIM Signing
Return to your email provider’s admin panel and enable DKIM authentication.
For example, in Google Workspace you click Start Authentication after DNS is added.
How to Verify DKIM
You can confirm DKIM in two ways:
Inside TrulyInbox, a checkmark under DKIM indicates proper setup
Use external tools like MailTester or DNS lookup tools to validate authentication
Common DKIM Issues
DNS propagation delays
Incorrect TXT record formatting
Wrong selector name
Weak key length
Forwarded emails breaking signatures
Key rotation errors
Careful setup prevents most issues.
Key Takeaway
DKIM is a core email authentication standard that protects your domain and improves deliverability.
When properly configured and combined with SPF and DMARC, DKIM significantly reduces spoofing risk and increases inbox trust.
It is essential for any domain sending business email.
Also check
Understanding DNS Records for Email Deliverability
What Is an SPF Record
DMARC: What, Why, and How to Set it up?
Technical Checklist Before Starting Email Warm-up
Did this answer your question?
😞
😐
😁