What Is an MX Record and How It Works
Learn what an MX record is, how it routes incoming emails, and why it is essential for reliable email delivery.
An MX record (Mail Exchanger record) is a type of DNS record that tells other mail servers where emails for your domain should be delivered.
Every domain that can receive email has at least one MX record. If you own multiple domains, each domain has its own MX records that control how incoming email is handled.
What Information Does an MX Record Contain
An MX record includes two key pieces of information.
The hostname of the mail server that should receive emails for the domain
A priority value that determines which server should be used first
These records work together to ensure emails are delivered reliably, even if one server is unavailable.
Why MX Records Are Important
MX records are essential for receiving emails. When someone sends an email to your domain, their mail server checks your domain’s MX records to find out where to deliver the message.
Without correct MX records, emails sent to your domain may bounce or never arrive.
MX records also help manage email delivery across different providers and improve reliability by allowing fallback servers when the primary server is unavailable.
MX Records and Email Providers
If you use a third party email service such as Google Workspace or Microsoft 365, your provider will give you specific MX records to add to your DNS settings.
These MX records usually point to the provider’s mail servers so they can receive emails on your behalf.
If you do not use a third party provider, you may have a single MX record pointing to your own mail server.
MX Record Priority and How It Works
MX records use priority values to determine which mail server should be contacted first.
Lower numbers indicate higher priority.
Higher numbers indicate lower priority.
When an email is sent to your domain, the sending mail server attempts delivery starting with the lowest priority number. If that server is unavailable, it moves on to the next one.
If multiple MX records share the same priority, the sending server can choose any of them, helping distribute load.
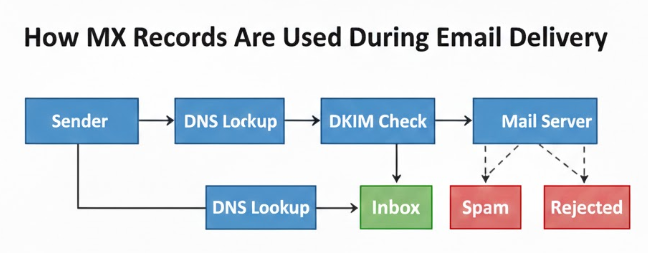
How MX Records Are Used During Email Delivery
When an email is sent, the sending mail server performs a DNS lookup on the recipient’s domain.
It retrieves the MX records and identifies the correct mail server based on priority. The email is then routed to that server for delivery.
This process happens automatically for every email sent across the internet.
How MX Records Are Queried in DNS
DNS queries are how systems locate resources on the internet.
When an email is being delivered, the receiving mail transfer agent queries DNS specifically for MX records instead of IP addresses.
This lookup returns the list of mail servers responsible for receiving emails for the domain, allowing proper routing of the message.
How to Check and Verify Your MX Records
It is good practice to regularly verify your MX records to ensure email delivery remains stable.
You can check your MX records by using DNS lookup tools or checking directly in your domain’s DNS management panel.
Regular monitoring helps detect misconfigurations early and prevents email delivery issues.
Key Takeaway
MX records control where emails sent to your domain are delivered. They are a foundational part of email infrastructure and must be correctly configured for reliable email reception.
Keeping MX records accurate and monitored ensures your domain can receive emails consistently and without disruption.
Also check
Understanding DNS Records for Email Deliverability
Google Workspace MX record values
How to Add an MX record in GoDaddy
Technical Checklist Before Starting Email Warm-up
Did this answer your question?
😞
😐
😁